Fixed Asset Turnover FAT: Definition, Calculation & Importance
By keeping an eye on this metric, you can identify risks early and take corrective action. It’s the ultimate spreadsheet add-on that gives stock investors instant access to financials. Keep in mind that a high or low ratio doesn’t always have a direct correlation with performance. There are a few outside factors that can also contribute to this measurement. This way, a fixed asset is turned into a service and becomes a variable asset.
Sending you timely financial stories that you can bank on.
Therefore, based on the above comparison, we can say that Y Co. is a bit more efficient in utilizing its fixed assets. The formula to calculate the total asset turnover ratio is net capital budgeting: what it is and how it works sales divided by average total assets. The fixed asset focuses on analyzing the effectiveness of a company in utilizing its fixed asset or PP&E, which is a non-current asset.
- Therefore, the above are some criterias that indicate why it is important to assess the fixed asset turnover ratio in any business.
- The fixed asset turnover ratio measures a company’s efficiency and evaluates it as a return on its investment in fixed assets such as property, plants, and equipment.
- The asset turnover ratio considers the average total assets in the denominator, while the fixed asset turnover ratio looks at only fixed assets.
Asset Turnover vs. Fixed Asset Turnover
Publicly-facing industries including retail and restaurants rely heavily on converting assets to inventory, then converting inventory to sales. Other sectors like real estate often take long periods of time to convert inventory into revenue. Though real estate transactions may result in high profit margins, the industry-wide asset turnover ratio is low. Fixed Asset Turnover is a crucial metric for understanding how well a company uses its fixed assets to drive revenue.
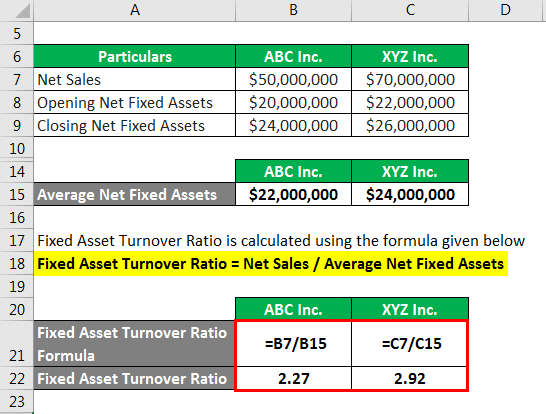
Fixed asset turnover ratio

Typically, a higher fixed asset turnover ratio indicates that a company has more effectively utilized its investment in fixed assets to generate revenue. The fixed asset turnover ratio is useful in determining whether a company uses its fixed assets to drive net sales efficiently. It is calculated by dividing net sales by the average balance of fixed assets of a period. Finally, companies may overlook the impact of depreciation on the fixed asset turnover ratio. Depreciation is a non-cash expense that reduces the value of fixed assets over time. If a company has a high level of depreciation, it can artificially inflate the fixed asset turnover ratio.
What Is a Good Fixed Asset Turnover Ratio?
With our online FAT Ratio calculator, you can examine the operational efficiency of any company by analyzing how well a company utilizes its fixed asset to generate revenue. The Fixed Asset Turnover Ratio (FAT) is found by dividing net sales by the average balance of fixed assets. Once this same process is done for each year, we can move on to the fixed asset turnover, where only PP&E is included rather than all the company’s assets. The Asset Turnover Ratio is a financial metric that measures the efficiency at which a company utilizes its asset base to generate sales. A high Fixed Asset Turnover ratio generally indicates that you’re generating a lot of sales relative to your assets, which can lead to better cash flow. Better cash flow means more flexibility and opportunities for your business.
InvestingPro: Access Fixed Asset Turnover Data Instantly
The fixed asset turnover ratio formula divides a company’s net sales by the value of its average fixed assets. The asset turnover ratio is a valuable financial metric that measures a company’s efficiency in using its assets to generate revenue. By understanding this ratio, you can gain insights into a company’s effectiveness in using its assets to drive sales. Another effective strategy to improve your fixed asset turnover ratio is to regularly assess the condition and performance of your fixed assets.
One way to measure this metric is to understand a business’s asset turnover ratio. Learn more about what exactly an asset turnover ratio is and how it’s calculated. Similarly, if a company doesn’t keep reinvesting in new equipment, this metric will continue to rise year over year because the accumulated depreciation balance keeps increasing and reducing the denominator. Thus, if the company’s PPL are fully depreciated, their ratio will be equal to their sales for the period. Investors and creditors have to be conscious of this fact when evaluating how well the company is actually performing. A high turn over indicates that assets are being utilized efficiently and large amount of sales are generated using a small amount of assets.
Companies should strive to maximize the benefits received from their assets on hand, which tends to coincide with the objective of minimizing any operating waste. That’s when my team and I created Wisesheets, a tool designed to automate the stock data gathering process, with the ultimate goal of helping anyone quickly find good investment opportunities. You might be wondering, “Why all the fuss about Fixed Asset Turnover?” Well, this isn’t just another number to gloss over. Diane Costagliola is a researcher, librarian, instructor, and writer who has published articles on personal finance, home buying, and foreclosure.
Your fixed assets at the beginning of the year were $200,000, and by the end, they were $250,000. As you can see, Jeff generates five times more sales than the net book value of his assets. The bank should compare this metric with other companies similar to Jeff’s in his industry. A 5x metric might be good for the architecture industry, but it might be horrible for the automotive industry that is dependent on heavy equipment.
Therefore, it is important to not only analyze the ratio itself, but also the underlying factors that may be influencing it. It is important to note that a high fixed asset turnover ratio may indicate that a company is efficiently using its fixed assets to generate revenue. However, a very high ratio may also suggest that the company is not investing enough in its fixed assets, which could lead to decreased productivity and revenue in the long run. On the other hand, a low fixed asset turnover ratio may indicate that a company is not using its fixed assets efficiently, which could lead to higher costs and decreased profitability.
